Kaizen là gì? Mà lại có sức mạnh khiến cho Toyata tồn tại và phát triển gần 150 năm mà gần như chưa từng sa thải một nhân viên nào? Nếu bạn đang tìm giải đáp cho câu trả lời trên thì cùng tìm hiểu qua bài viết sau nhé!
Trong bài viết này, DPS sẽ giải thích chi tiết cho bạn các vấn đề xoay quanh Kaizen theo trình tự sau:
- Kaizen là gì?
- Câu chuyện thực tế – Toyota áp dụng Kaizen vào quản trị.
- Doanh nghiệp có lợi ích gì khi áp dụng Kaizen?
- Các bước thực hiện Kaizen.
- Những yếu tố quyết định đến sự thành công khi thực hiện triết lý Kaizen.
- Các nguyên tắc của Kaizen khi áp dụng là gì?
1. Kaizen là gì?

Khi đề cập đến khía cạnh cải tiến chất lượng, bạn không thể nào bỏ qua Nhật Bản. Đây là một quốc gia đi đầu về khả năng này. Khá nhiều doanh nghiệp tại Nhật đã ứng dụng thành công các triết lý và văn hoá kinh doanh. Và Kaizen là một trong số ấy. Vậy Kaizen là gì?
Kaizen thực ra là một thuật ngữ kinh tế và có nguồn gốc từ Nhật Bản. Nó được ghép lại bởi hai từ. Trong khi “Kai” có nghĩa là thay đổi và từ “Zen” có nghĩa là tốt hơn. Tựu trung lại Kaizen có nghĩa là “thay đổi để tốt hơn” hoặc bạn có thể hiểu là “cải tiến liên tục”.
Đây chính là một trong những triết lý kinh doanh nổi tiếng tại xứ sở mặt trời mọc từ những năm 1950s (Álvarez-García, 2018). Kaizen không chỉ được các doanh nghiệp tại Nhật áp dụng thành công mà còn được sử dụng trên toàn thế giới. Do đó mà thuật ngữ này được dịch trong tiếng anh là” continuous improvement” (Carnerud, 2018) – “ cải tiến liên tục”.
Nhiều người vẫn lầm tưởng Kaizen với thuật ngữ “Innovation”- “Đổi mới” ở các nước phương tây. Trên thực tế, sự thay đổi của Kaizen hướng đến con người, những cải tạo trên quy mô khá nhỏ với tính chất tăng dần và đạt được mục tiêu theo thời gian dài. Điều này hoàn toàn khác với “Innovation” mà phương tây áp dụng.
2. Câu chuyện thực tế – Toyota áp dụng Kaizen vào quản trị.

Trong lịch sử hình thành và phát triển của mình, Toyota đã không ít lần trải qua những biến cố và khó khăn phải đối mặt. Có thể kể đến như: cuộc khủng hoảng tài chính 2008 hay những ảnh hưởng nặng nề từ trận động đất khủng khiếp tại Nhật Bản và sóng thần lịch sử tại Thái Lan. Tuy nhiên, ngay những lúc khó khăn nhất và đối mặt với nguy cơ phá sản thì Toyota vẫn nhất quyết duy trì chính sách “nói không với sa thải nhân viên”
2.1. Chấp nhận trả thêm 220 triệu USD/năm lãi vay và thà cắt giảm chi phí chứ không cắt giảm nhân viên.
Trong cuộc khủng hoảng tài chính Châu Á vào năm 1997, Toyota Thái Lan đã trải qua 4 năm thua lỗ liên tiếp mà vẫn không hề cắt giảm việc làm.
Quyết định này được đưa xuống từ người nắm giữ cương vị cao nhất của Toyota lúc bấy giờ. Đó là chủ tịch Hiroshi Okuda. Ông Okuda đã ra lệnh: “Cắt giảm tất cả các chi phí, nhưng không được chạm vào bất kỳ người nào”.
Cũng do chính sách này mà vào tháng 8 năm 1998, Moddy đã hạ mức hạng tín của Toyota xuống AA1 from AAA. Việc này đồng nghĩa với việc Toyota phải đi vay với lãi xuất cao hơn và tiêu tốn lên đến 220 triệu USD hằng năm. Mặc dù vậy nhưng Toyota cũng không cam kết từ bỏ cam kết về chính sách đảm bảo việc làm cho nhân sự của mình.
2.2. Lý giải vì sao Toyota tồn tại được gần 150 năm mà gần như không đuổi một người nào?
Kaizen được ứng dụng bởi Toyota. Đây vốn là một hệ thống được sinh ra tại nơi sản xuất. Nhưng triết lý này cũng được xem như hệ thống đào tạo con người biết suy nghĩ. Thông qua đó, Toyota tạo ra những cơ hội để nhân viên phát huy trí tuệ.
Để một ai đó hành động thì họ phải là người đóng góp ý kiến. Khi tự mình đưa ra ý kiến thì họ sẽ tự tin và biết hành động theo hướng tích cực.
Câu hỏi đặt ra là làm thế nào để một người đóng góp ý kiến? Đơn giản, người lãnh đạo hãy cố tình “làm khó” họ một chút. Một khi đối diện với thử thách hay khó khăn thì con người buộc phải suy nghĩ và đưa ra cách giải quyết vấn đề.
2.3. Câu chuyện thú vị về sự ra đời của dòng xe Soluna

Khi bắt tay vào thiết kế và xây dựng dòng xe chiến lược tại Châu Á, dòng xe Tercel (hay còn biết đến với cái tên Soluna tại Thái Lan). Ông Takeshi Yoshida, kỹ sư trưởng, đã đưa ra cách làm thú vị như sau:
Dòng xe Soluna dự định bán ở Thái. Yêu cầu đặt ra ở đây cho các kỹ sư là phải thiết kế một mẫu xe có giá bán đương thời thấp hơn so với dòng xe Corolla. Tuy nhiên, trong nhận thức của nhiều nhân viên thì Corolla là dòng xe thuộc mức thấp nhất trong các dòng xe của Toyota.
Do vậy mà nhân viên không thể hình dung ra nếu sản xuất xe dưới cả dòng xe Corolla thì sẽ là thứ gì. Vậy nên khi được hỏi:” Có thể loại bỏ được phần nào từ Corolla không?” Thì mọi người đều trả lời là không thể.
Không lâu sau ông Yoshida đã cố tình làm ra mẫu xe có giá rất rẻ và tệ để mang đến cho họ xem. Khi được “chiêm ngưỡng” chiếc xe “giẻ rách” này; thì hàng loạt ý kiến được đưa ra.
Từ ý tưởng tồi tệ của ông Yoshida mà đã kiến tạo ra được nhiều ý tưởng hay từ mọi người. Và kết quả là mẫu xe Soluna đã đời.
Kaizen theo phong cách Toyota chính là lấy trí tuệ của con người làm gốc. Vai trò của người lãnh đạo là tạo ra mội trường để “lôi và kéo” những trí tuệ đó ra và gom chúng lại. Tích luỹ những Kaizen nhỏ sẽ cho ra những thành quả bất ngờ về lâu dài.
3. Doanh nghiệp có lợi ích gì khi áp dụng Kaizen?

When Kaizen được áp dụng linh hoạt và hợp lý vào doanh nghiệp; nó sẽ mang đến nhiều lợi ích hữu hình lẫn vô hình. Thế lợi ích của Kaizen là gì? Cùng DPS tìm hiểu nhé!
3.1. Lợi ích hữu hình đối với doanh nghiệp
Có 2 lợi ích hữu hình điển hình nhất đối với doanh nghiệp khi ứng dụng thành công Kazen.
Thứ nhất, doanh nghiệp bạn sẽ giảm được sự lãng phí; song song với ấy là làm tăng năng suất sản xuất cho doanh nghiệp của bạn. Trong case của Toyota, Kaizen đa giúp công ty cắt giảm được hao phí như: hàng tồn kho, thời gian chờ đời, vận chuyển và sản xuất dư thừa tại các phân xưởng.
Thứ hai là doanh nghiệp còn cải thiện được hoạt động trong quá trình vận hành của mình. Thực vậy, tại các phân xưởng sản xuất của Toyota, người công nhân không mất thời gian để phân loại các bộ phận phụ tùng. Họ chỉ việc sử dụng dùng giỏ nhựa để phân loại. Ngoài ra, họ còn tự chế tạo xe chuyên chở từ các bộ phận có sẵn trong dây chuyền và chỉ việc lắp đặt thêm động cơ. Nhờ vậy mà Toyota đã có thể tiết kiệm khoảng 3000 USD cho chi phí mua xe chở hàng.
Có thể nhận thấy rằng, doanh nghiệp sẽ có thể tích lũy từng cải tiến nhỏ nhất trong thời gian dài; để rồi từ đó tạo ra được những kết quả to lớn hơn.
3.2. Lợi ích vô hình đối sự phát triển của doanh nghiệp
Không những mang lại lợi ích hữu hình mà Kaizen còn đem đến 3 lợi ích vô hình nổi bật cho doanh nghiệp.
Đầu tiên là mỗi nhân viên được khuyến khích và tạo động lực để đưa ra ý tưởng hay mang đến nhiều cải tiến hiệu quả trong doanh nghiệp.
Lợi ích thứ hai là, nâng cao tinh thần làm việc tập thể cho toàn thể nhân viên. Đồng thời còn làm tăng tính đoàn kết trong nội bộ doanh nghiệp.
Cuối cùng là hình thành văn hoá tiết kiệm và không ngừng cải tiến trong doanh nghiệp.
4. Các bước thực hiện Kaizen.
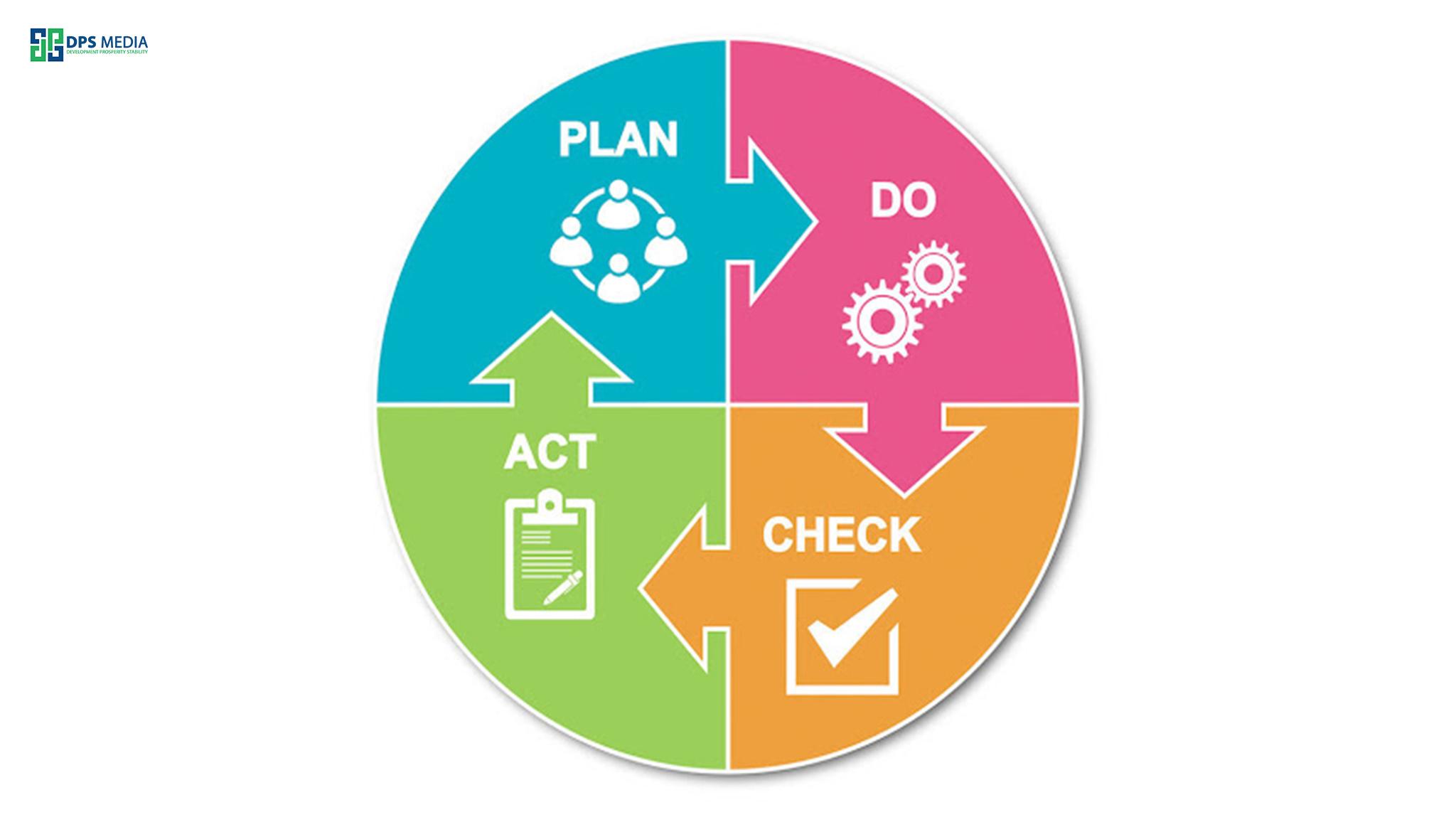
Bây giờ hẳn là bạn đã cơ bản hiểu được Kaizen là gì rồi đúng không nào! Bước kế tiếp, DPS sẽ giới thiệu cho các bạn làm thế nào để ứng dụng hiệu quả triết lý vào doanh nghiệp của bạn!
Kaizenđược thực hiện dựa trên chu trình PDCA (Plan – Do – Check – Action). Và nó được gói gọn trong 8 bước. Cụ thể hơn, các bước thực hiện Kaizen including:
Bước 1: Lựa chọn phạm vi áp dụng co Kaizen.
Doanh nghiệp nên lưu ý khi lựa chọn phạm vi để áp dụng Kaizen. Ở đây, phạm vi có thể là một dây chuyền sản xuất hay một bộ phận chuyên môn. Và bạn nên đảm bảo rằng tính khả thi khi thực hiện cải tiến.
Để đạt độ chắc chắn được cao hơn, hãy thử nghiệm triết lý này ở một điểm nhất định; rồi sau đó bạn có thể mở rộng từ từ ra đến khi nào đạt được quy mô toàn doanh nghiệp.
Bước 2: Tìm hiểu thực trạng hiện tại và xác định mục tiêu cho doanh nghiệp.
Trước khi lập chiến lược truyên thông IMC hay bất kỳ một chiến lược nào thì bạn luôn cần phải tìm hiểu và đánh giá tình trạng thực tế của doanh nghiệp mình. Từ đó, bạn mới có thể đưa ra một mục tiêu thống nhất, có tính cơ sở và khả thi hơn.
Điều này sẽ giúp doanh nghiệp bạn tránh được các vấn đề lãng phí, tận dụng hiệu các nguồn lực và thực hiện dang dở kế hoạch.
Bạn nên nhớ rằng Kaizen là một triết lý chứ không phải là một công cụ. Do đó, nó đòi hỏi một sự cam kết và nỗ lực lâu dài của mọi thành viên và mọi cấp bậc trong doanh nghiệp.
Bước 3: Phân tích dữ liệu đã thu thập và xác định nguyên nhân cốt lỗi.
Sau khi thu thập được các dữ liệu liên quan và cần thiết, cấp lãnh đạo nên họp lại với nhau để xem xét và đánh giá thực trạng hiện tại của doanh nghiệp. Quan trọng nhất là họ có thể cùng nhau xác định những nguyên nhân cốt lỗi của vấn đề.
Bước 4: Dựa trên cơ sở phân tích dữ liệu để xác định biện pháp thực hiện
Khi tìm ra được gốc rễ của vần đề, thì việc tiếp theo cần thực hiện là đưa ra giải pháp. Song song với giải pháp là những tiêu chí và công cụ để đo lường kết quả đạt được.
Bước 5: Thực hiện biện pháp Kaizen
Đây là bước mà triết lý Kaizen được áp dụng theo kế hoạch ban đầu đã đề ra. Trong quá trình thực hiện, ban lãnh đạo nên tạo ra môi trường phù hợp để nhân viên đóng góp ý kiến. Đồng thời, họ cũng là người tập hợp những ý kiến phù hợp, kiểm tra thường xuyên, và giám sát việc áp dụng vào thực tế của doanh nghiệp.
Bước 6: Xác nhận kết quả thực hiện biện pháp
Khi biện pháp đã được thực hiện thì doanh nghiệp cần phải thu thập dữ liệu liên quan. Nhằm mục đích đo lường và đánh giá kết quả thực hiện. Ở bước này, bạn sẽ sử dụng công cụ phù hợp để so sánh kết quả đạt được với các tiêu chí đã đặt ra ở Bước 4.
Bước 7: Xây dựng hoặc sửa đổi các tiêu chuẩn để khắc phục nhược điểm
Một khi đánh kết quả thực hiện, doanh nghiệp có thể tìm ra một số nhược điểm hoặc những điểm chưa phù hợp khi áp dụng Kaizen vào thực tiễn của doanh nghiệp. Ngay lập tức, ban lãnh đạo có thể điều chỉnh hoặc những biện pháp phù hợp hơn. Nhằm tránh việc áp dụng Kaizen một cách máy móc vào doanh nghiệp bạn.
Bước 8: Xem xét các quá trình trên và xác định dự án tiếp theo
Như DPS đã nhấn mạnh ở trên, Kaizen là một triết lý cần một thời gian tương đối dài để nhận thấy kết quả. Ghi nhớ điều ấy và doanh nghiệp không nên nóng vội mà phải kiên nhẫn thực hiện những điều nhỏ nhăt nhất và rút kinh nghiệm sâu sắc qua mỗi lẫn thực hiện. Làm được điều này chắc hẳn về lâu dài, doanh nghiệp có thể gặt hái được những thành tựu to lớn hơn.
5. Những yếu tố quyết định đến sự thành công khi thực hiện triết lý Kaizen.

Việc hiểu được Kaizen là gì là một chuyện. Nhưng khi ứng dụng nó vào thực tiễn và thành công lại là một chuyện khác. Bởi lẽ, triết lý này còn bị ảnh bởi 3 yếu tố tối quan trọng sau:
5.1. Sự cam kết của cấp lãnh đạo cao nhất
Trong tiết lý Kaizen, vai trò nhà lãnh đạo được đặc biệt chú trọng. Do bởi, nhà lãnh đạo là người lèo lái “còn thuyền”. Họ cần tạo ra môi trường phù hợp để nhân viên có thể kiến tạo ý tưởng như:
- Làm việc nhóm.
- Quản lý theo mạng lưới.
- Đầu tư vào chất xám.
- Đào tạo nhân viên.
5.2. Vai trò của người quản lý và team leader
Đối với team leaders hay người quản lý, họ cần phải duy trì và cải tiến liên tục các chuẩn mực hiện hành về công nghệ cũng như điều hành sản xuất. Việc này nhằm mục đích là đạt được năng suất lao động cao hơn. Sau đó, kết quả kinh doanh được tốt hơn.
5.3. Nỗ lực tham gia đóng góp của mọi người
Sự thành công của việc ứng dụng Kaizen vào doanh nghiệp quyết định rất bởi sự tham gia và đóng góp của tất cả nhân viên. Dù cho ở cấp bậc nào thì họ cũng đều phải nhận thức được tầm quan trọng của triết lý này. Mỗi nhân viên trong tổ chức đều nỗ lực tham gia và đóng góp ý kiến để thiết lập hệ thống tư duy mới và đồng lòng xây dựng một môi trường kinh doanh đúng hướng. Câu nói: “ Muốn đi nhanh thì đi một mình. Muốn đi xa thì đi cùng nhau” rất đúng trong trường hợp này.
6. Các nguyên tắc của Kaizen khi áp dụng là gì?

Sở dĩ, triết lý Kaizen trở nên phổ biến rộng rãi như ngày nay là vì nó sở hữu những nguyên tắc bất biến theo thời gian. Một khi doanh nghiệp đã áp dụng Kaizen thì phải nhất nhất tuân thủ theo. Bất kể quy mô của doanh nghiệp bạn là nhỏ hay lớn. Chi tiết hơn thì Kaizen có 10 nguyên tắc sau bao gồm:
Nguyên tắc 1: Luôn tập trung vào lợi ích của khách hàng
Tất cả sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ của doanh nghiệp được tạo ra phải đáp ứng được nhu cầu khách hàng mục tiêu. Do đó, doanh nghiệp cần tập trung vào việc cải tiến từng chút một trong chất lượng sản phẩm hay dịch vụ. Đồng thời làm gia tăng lợi ích mang lại của sản phẩm; nhằm mục đích sao cùng là tạo được hài lòng và thoả mãn tối đa từ khách hàng.
Nguyên tắc 2: Không ngừng cải tiến
Hoàn thành mục tiêu ban đầu không có nghĩa công việc cải tiến kết thúc. Đây chỉ là sự kết thúc của một giai đoạn; trước khi chuyển tiếp sang giai đoạn tiếp theo.
Vì nhu cầu của khách hàng sẽ càng ngày càng tăng lên trong tương lại. Vậy nên, nếu không muốn bị đào thải khỏi thị trường thì doanh nghiệp cần không ngừng cải tiến để nâng cao chất lượng sản phẩm. Vừa giúp doanh nghiệp tiết kiệm thời gian và chi phí. Đồng thời, doanh nghiệp có thể đi trước đón đầu hay tạo ra xu hướng. Tức là tạo ra nhu cầu cho khách hàng ngay cả khi họ chưa nhận ra nhu cầu của họ.
Nguyên tắc 3: Xây dựng văn hóa không đổ lỗi
Mỗi nhân viên được giao một nhiệm vụ cụ thể. Khi mắc sai lầm hoặc không hoàn thành nhiệm vụ được giao thì trách nhiệm cần được quy về đúng người. Không đổ lỗi cho người khác hoặc đưa những lý do không chính đáng.
Nguyên tắc 4: Thúc đẩy văn hóa doanh nghiệp mở
Văn hóa doanh nghiệp mở ở đây được hiểu là khi nhân viên dám nhìn thẳng vào sai sót cũng như khuyết điểm của bản thân họ. Nếu một nhân viên cần sự giúp đỡ từ đồng nghiệp hay cấp trên thì họ cần chủ động tìm kiếm sự giúp đỡ từ mọ người.
Do đó, doanh nghiệp cần thiết lập một mạng lưới truyền thông nội bộ. Nơi mà các nhân viên có thể giúp đỡ, học hỏi và chia sẻ kinh nghiệm lẫn nhau.
Nguyên tắc 5: Khuyến khích làm việc nhóm theo triết lý Kaizen
Doanh nghiệp nên định hướng xây dựng cấu trúc nhân sự theo các đội nhóm làm việc hiệu quả, thay vì làm việc các nhân.
Khi thành lập các nhóm cần phải phân quyền rõ ràng. Đồng thời, họ cần có những quy ước để giải quyết những mâu thuẫn xảy ra trong team.
Trong đó, team leader cần có năng lực lãnh đạo. Trong khi mỗi thành viên trong nhóm cần tôn trọng quy ước và tính cách của nhau.
Nguyên tắc 6: Kết hợp nhiều bộ phận, chức năng trong cùng dự án
Khi thực hiện một dự án bất kỳ, doanh nghiệp hãy phân bố và kết hợp nguồn nhân lực từ các bộ phận phòng khác. Nếu cần thiết, bạn hoàn toàn có thể tận dụng thêm nguồn lực từ bên ngoài.
Nguyên tắc 7: Tạo lập các mối quan hệ đúng đắn giữa toàn bộ nhân viên
Để không tạo dựng các mối quan hệ đối đầu hay thù địch; thì doanh nghiệp cần đầu tư vào những chương trình đào tạo kỹ năng giao tiếp cán bộ nhân viên. Ngoài ra, doanh nghiệp có thể tổ chức những buổi team-building để thắt chặt hơn mối quan hệ giữa các nhân viên.
Việc xây dựng mối quan hệ giữa các nhân viên; cũng tương đồng với việc xây dựng được văn hoá tại doanh nghiệp của bạn.
Nguyên tắc 8: Rèn luyện ý thức kỷ luật và tinh thần tự giác
Xây dựng và rèn luyện cho nhân viên ý thức kỷ luật cũng như tinh thần tự giác tuân thủ các quy tắc tại doanh nghiệp.
Bên cạnh đó, nhân viên cũng cần đặt lợi ích công việc lên trên hết. Từ đó, họ có thể tự đánh giá và xem xét lại chính bản thân. Việc này nhằm mục đích là để họ có thể tự cải thiện và khắc phục điểm yếu của mình.
Nguyên tắc 9: Thông tin đến mọi cấp bậc và nhân viên
Nếu muốn đạt được kết quả cao trong công việc; thì doanh nghiệp nên minh bạch thông tin với các nhân viên của mình.
Bởi thông tin là yếu tố quan trọng hàng đầu len lỗi và “chảy” xuyên suốt trong quá trình kinh doanh. Thông tin được truyền đạt tốt trong nội bộ sẽ là cách hoàn hảo; để doanh nghiệp chia sẻ khó khăn và thách thức chung đến với mọi nhân viên trong tổ chức.
Nguyên tắc 10: Thúc đẩy năng suất cũng như hiệu quả làm việc
Triển khai đồng loạt và tổng hợp phương pháp đào tạo nội bộ đến các phòng ban trong doanh nghiệp.
Trong mỗi dự án, cần phải phân quyền cụ thể và rõ ràng cho mỗi vị trí tới từng thành viên trong nhóm. Mỗi cá nhân đều phải tự phát huy khả năng của mình, chủ động đưa ra ý kiến đóng góp và phản hồi.
Khi có thành tích thì doanh nghiệp cần công nhận và khen thưởng kịp thời đến mọi thành viên trong đội nhóm. Việc này sẽ kích thích năng lực cũng như nâng cao hiệu quả làm việc trên quy mô toàn doanh nghiệp.
Hy vọng bài viết trên đã cung cấp cho các bạn những thông tin hữu ích xoay quanh triết lý Kaizen. Chúc bạn áp dụng thành công triết lý nào vào doanh nghiệp của mình!
Nguồn tham khảo:
Álvarez-García, J. D.-S. (2018). Systematic bibliometric analysis on Kaizen in scientific journals. The TQM Journal.
Carnerud, D. J. (2018). Kaizen and continuous improvement–trends and patterns over 30 years. The TQM Journal.






