In the era of automation and system integration, synchronizing data between different platforms is one of the most common yet challenging tasks. Whether you have a customer list from CRM, a product table from an Excel file, or sensor data from IoT, and you need to bring them into your Supabase database.
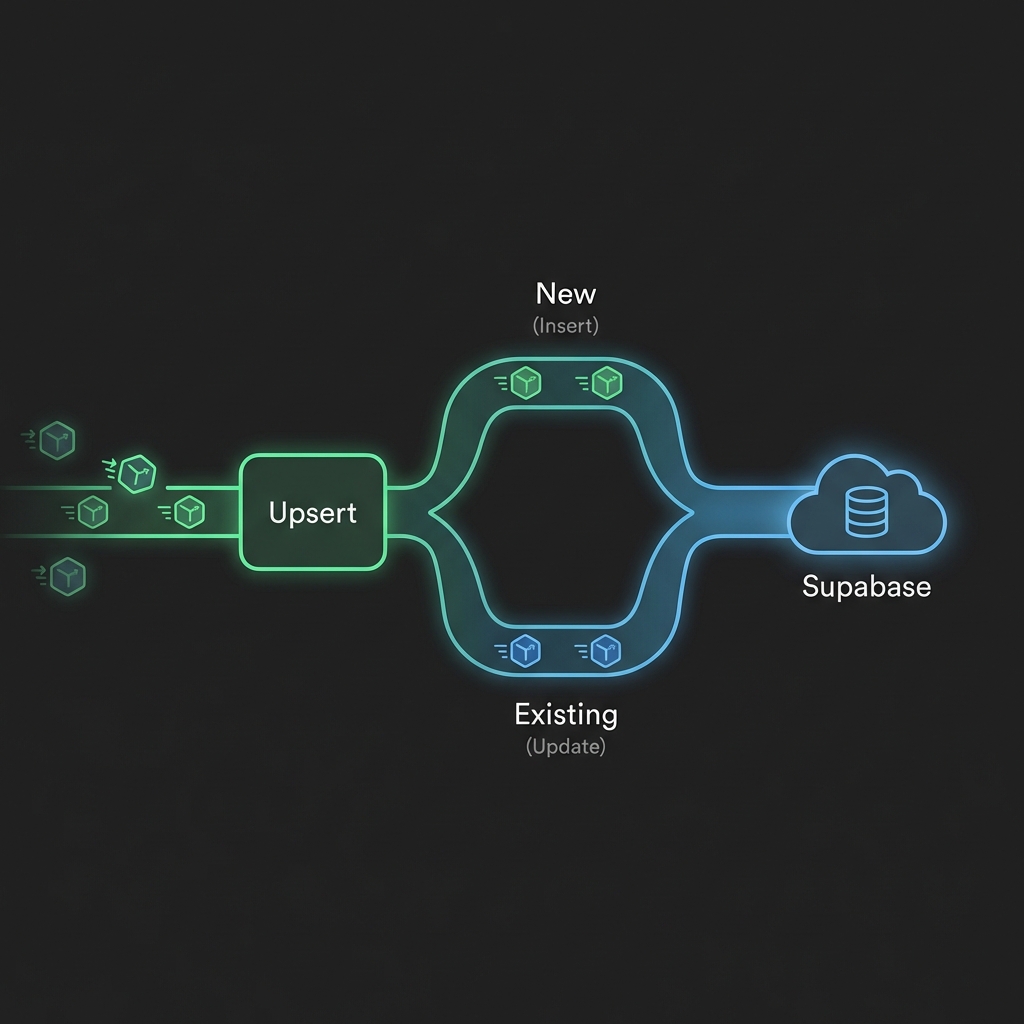
The problem arises when you have to answer the question: “Does this data already exist?”. If not, you need to Insert. If yes, you need to Update. This process is called Upsert.
In this article, we will dive deep into how to use the custom Supabase Upsert node in n8n to solve this problem thoroughly, efficiently, and with optimal performance.
The pain of manual data synchronization
Before diving into the solution, let's review how we traditionally handle this issue in n8n. Usually, you have to build a quite cumbersome workflow:
- Fetch source data: Read from Google Sheets, Webhook, or API.
- Query in Supabase: Use a Supabase node to “Select” to check if the record with the corresponding ID already exists.
- Check condition (IF node):
- If returned data is empty (True) -> Go to branch Insert.
- If data is returned (False) -> Go to branch Update.
- Execute: Run the corresponding Insert or Update node.
This approach has many fatal disadvantages:
- Resource-intensive: You must make at least 2 requests (Select + Insert/Update) for each data row.
- Slow: When processing thousands of rows, network latency will make the workflow run very slowly.
- Hard to maintain: Workflow becomes complex with tangled connections, prone to logic errors.
- Race Condition risk: In a multi-threaded environment, two processes may check and both find the data doesn't exist, leading to both Inserting and causing duplicate errors.
Solution: Custom Supabase Upsert Node
Node Supabase Upsert customizable is designed to completely eliminate the above complexities. It encapsulates the entire “Check and Decide” logic into a single operation at the database level.
Instead of n8n having to “ask” Supabase first then “do”, n8n just “commands”: “Ensure this data is in the table, update if exists, create if not”. Supabase handles the rest.
Why this Node excels?
- Maximum performance: Reduce API calls by half or even 1000 times with Batch mode.
- Simplify Workflow: Replace 3-4 complex nodes with a single node.
- Atomicity: Ensure data integrity, avoid Race Condition errors.
Breakthrough features
Let's dive deeper into the features this node provides:
1. Automatic Upsert based on unique key
The core power of the node lies in its ability to identify the “identity” of the record. Through the “On Conflict” parameter, you specify which column contains the unique value (Unique Key).
Example: If syncing users, “email” is unique. You enter “email” in “On Conflict”. When n8n sends a user with email “test@example.com”:
- If Supabase doesn't find “test@example.com” -> Create new user.
- If found -> Update other information (name, age, address...) of that user.
2. Batch Processing
This is the “killer” feature for Big Data tasks. When you enable the option Send All Items, the node will not send items one by one. Instead, it collects all input items (e.g., 5000 products) into a giant JSON array and sends them in a single request.
This reduces execution time from minutes to just seconds.
3. Conflict Resolution Strategy
Update is not always what you want. The node provides 2 strategies:
- Merge (Default): Standard Upsert behavior. New data will overwrite old data. Suitable for synchronizing the latest state.
- Ignore: “Keep original”. If the data already exists, Supabase will do nothing, only Insert new rows. Suitable for importing historical data or logs, where you don't want to change what has been recorded.
4. Flexible data sources
You can use data from:
- Input Items: Standard data flowing from previous nodes in n8n.
- JSON Raw: Directly enter JSON string or use Expression to customize complex data structures without needing “Function” or “Set” nodes beforehand.
Detailed step-by-step configuration guide
To help you master this node, let's go through each configuration parameter:
Step 1: Connection (Credentials)
You need to create a new Credential of type “Supabase Upsert API”.
- Project URL: Find in Settings -> API of the Supabase dashboard. Format “https://xyz.supabase.co”.
- Service Role Key: Important note, you should use the “service_role” key instead of the “anon” key to have permission to bypass RLS (Row Level Security) when necessary and perform bulk write operations without permission limits.
Step 2: Select Table
After connecting, the node will automatically load the list of tables in your database. Please select the correct target table, e.g., “products” or “customers”.
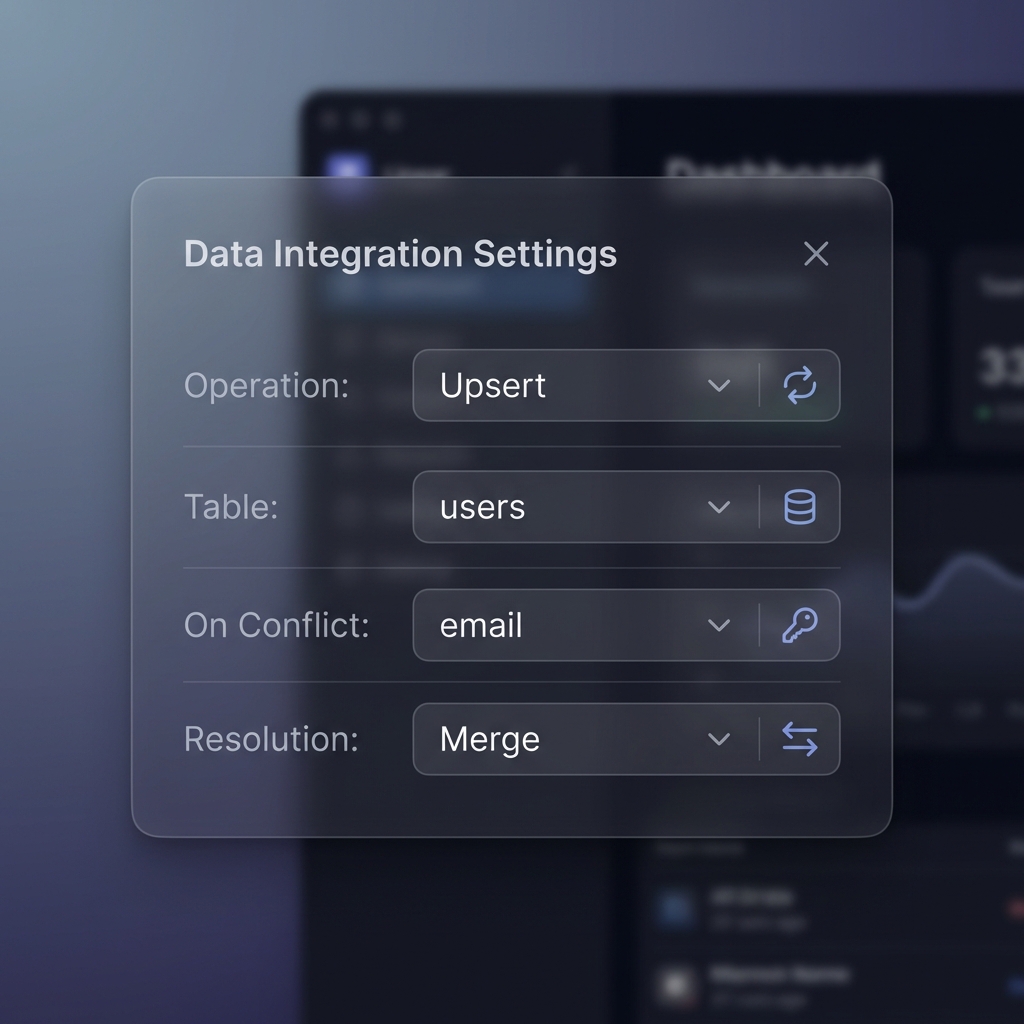
Step 3: Upsert Configuration (Most Important)
- On Conflict: Enter the name of the column with unique constraint (Unique Constraint).
- Tip: If you use a composite primary key (Composite Key, e.g., order_id + product_id), enter them separated by commas: order_id, product_id.
- Resolution:
- Select “Merge” to always update the latest value.
- Select “Ignore” if you only want to insert new data.
Step 4: Advanced Options
- Return: Select “Representation” for the node to return the data just Inserted/Updated (useful for getting auto-generated IDs). Select “Minimal” if you don't care about the return result to save network bandwidth.
Real-world application scenarios (Use Cases)
Scenario 1: E-commerce Inventory Sync (High Volume)
You have a CSV file containing 10,000 products from the main warehouse, updated every hour.
- Configuration:
- Table: “inventory”
- On Conflict: “sku” (Product Code)
- Resolution: “Merge”
- Send All Items: “True”
- Results: Update inventory quantity for 10,000 products in just 1-2 seconds. New SKUs will be automatically added to the sales system.
Scenario 2: Lead Collection from Landing Page
You run ads on multiple channels, data pours into Webhook. A customer may register multiple times.
- Configuration:
- Table: “leads”
- On Conflict: “email”
- Resolution: “Ignore”
- Results: You only keep information from the first registration (First Touch Attribution). Subsequent registrations will be ignored, avoiding dilution of CRM data.
Scenario 3: IoT Sensor Logging
The sensor system sends temperature every 5 minutes. Sometimes the network is unstable, the sensor resends old packets.
- Configuration:
- Table: “sensor_readings”
- On Conflict: “device_id, timestamp”
- Resolution: “Merge”
- Results: Ensure that at any time, each device has only one correct record. If data is resent, it will overwrite the old one (usually identical), keeping the database clean.
Common notes and risks
- “On Conflict” Error”: If you enter the wrong column name or that column does not have a “UNIQUE” constraint in the database, Supabase will report an error. Make sure you have created a Unique Index for that column in the SQL Editor.
- SQL to create index: CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_users_email ON public.users (email);
- Request Size Limit: Although “Send All Items” is very powerful, Supabase has a body size limit (usually a few MB). Sending 100,000 rows at once may cause errors. Please split (Split in Batches) into batches of 1,000 – 5,000 rows.
- Access Rights (RLS): If using “anon” key, ensure you have configured Row Level Security to allow Insert/Update. Best for backend workflow is to use “service_role” key.
Conclusion
Node Supabase Upsert not just a utility tool, it is the “backbone” for high-performance data integration processes in n8n. Understanding and applying this node correctly will save you hours of debugging, reduce server load, and bring a smooth experience to the system.
If you are building complex automation systems with Supabase, this is definitely the node you cannot miss. Install, experience, and feel the superior speed today!












